**Physician Burnout: An Escalating Crisis in American Healthcare**
**Introduction**
Physician burnout in the United States is being increasingly acknowledged as a crisis with considerable adverse effects on healthcare delivery and the welfare of healthcare professionals. Initially defined by Herbert Freudenberger in 1977, burnout is marked by emotional fatigue, depersonalization, and diminished personal achievement. Its detrimental impact on the quality of care delivered by healthcare professionals and their overall health has been documented.
**The Prevalence of Burnout**
More than 50 percent of physicians and numerous trainees within the American healthcare system are impacted by burnout. Despite growing awareness and improved access to mental health support, the repercussions of burnout continue to be widespread.
**Alarming Suicide Rates**
In the U.S., nearly 300 to 400 physician suicides occur each year, averaging one physician suicide daily. This scenario is comparable to disasters such as the crash of a Boeing 747 annually. The CDC indicated a general ratio of 35 attempts for every completed suicide, implying about 14,000 physician suicide attempts each year, affecting roughly 1.4 percent of the U.S. physician population.
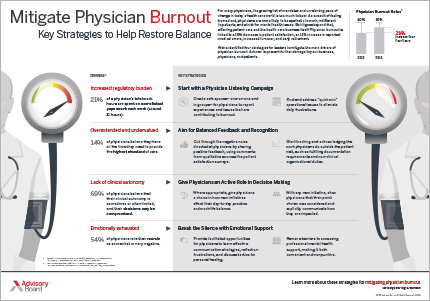
**Strategies for Burnout Reduction**
Numerous healthcare systems are striving to mitigate burnout through various preventative measures. A 2016 study by Wendy Awa and colleagues revealed that 80 percent of institutions tackling burnout succeeded in lowering its occurrence. Prominent institutions like the Mayo Clinic and Vanderbilt University have established dedicated programs providing resources for burnout prevention and management.
**The Importance of Education**
Combating physician burnout begins with reforming educational approaches in medical schools. A continuous course titled something akin to “The Successful Medical Practice” is suggested, concentrating on recognizing and preventing burnout. This initiative would stress the importance of sustaining mental well-being, promoting the utilization of mental health resources, and enhancing doctor-patient interactions.
**Conclusion**
To effectively address physician burnout, a firm commitment from institutions starting at medical education is vital. Alleviating burnout can improve both physician well-being and the quality of care within America’s healthcare system.