# Endometriosis and Infertility: Understanding Mechanisms and Treatment Approaches
## Introduction
Endometriosis is a persistent, estrogen-dependent inflammatory condition impacting approximately 10% of women of reproductive age. It is a significant factor contributing to infertility, yet is often underrecognized and inadequately addressed. This article delves into the ways endometriosis affects fertility, examines treatment alternatives, and assesses how dietary and lifestyle changes can influence reproductive health.
## The Link Between Endometriosis and Infertility
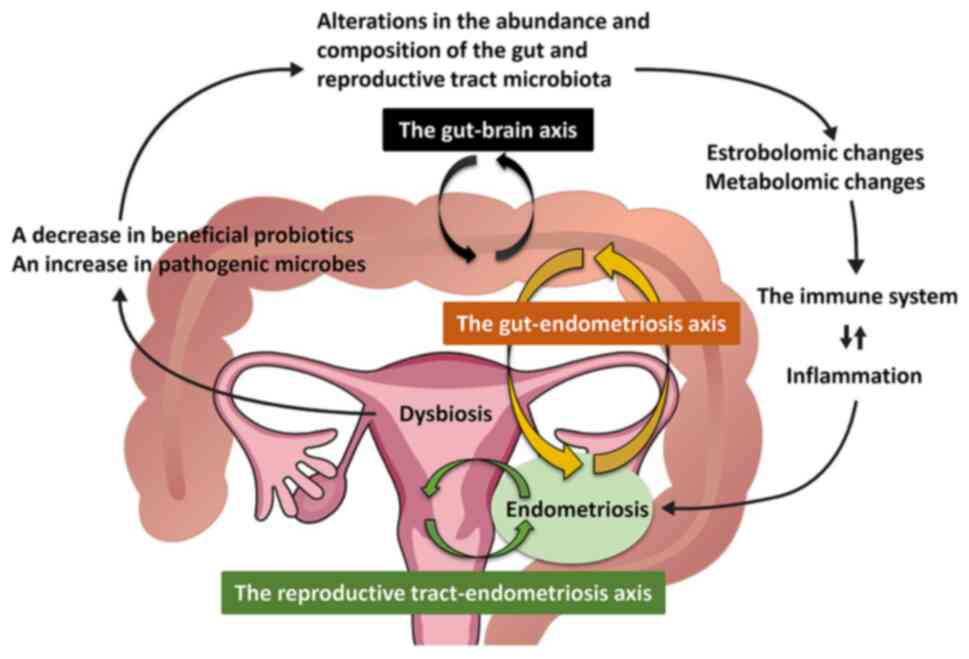
Endometriosis arises when tissue resembling the endometrium develops outside the uterus, predominantly on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and peritoneum. This abnormal tissue proliferation is linked to chronic pelvic pain, intense menstrual discomfort, and fertility issues. The condition is classified into four stages based on its severity, with fertility generally declining as the condition advances.
### Pathophysiology of Endometriosis-Related Infertility
Endometriosis can compromise fertility through various interrelated pathways:
– **Pelvic Adhesions and Anatomical Distortion:** Scar tissue and adhesions may obstruct the fallopian tubes or shift reproductive organs, hindering the movement of eggs and sperm.
– **Diminished Ovarian Reserve:** Ovarian endometriomas (chocolate cysts) inflict damage on healthy ovarian tissue, resulting in a reduced ovarian follicle pool and fewer viable eggs.
– **Inflammatory Microenvironment:** Chronic inflammation leads to increased levels of cytokines and other immune factors that interfere with implantation and embryo development.
– **Oxidative Stress:** The presence of reactive oxygen species (ROS) causes damage to oocytes, resulting in DNA fragmentation, impaired mitochondrial function, and reduced fertilization potential.
– **Altered Immune Function:** Disruption of the immune system impacts sperm longevity and hampers successful embryo implantation.
## Clinical Management Strategies
### Surgical Management: Laparoscopy and GnRH Agonists
Laparoscopic excision of endometriotic lesions is considered the gold standard for managing symptomatic endometriosis and enhancing fertility outcomes. The objective of surgery is to restore normal pelvic anatomy and remove adhesions. Post-surgery use of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH) agonists can aid in mitigating disease recurrence and improving pregnancy rates.
### Hormonal Suppression Therapy
Hormonal treatment is pivotal in addressing endometriosis-related infertility, especially in scenarios where surgery is not feasible or if recurrence happens postoperatively. Common strategies include:
– **GnRH Agonists:** Reduce estrogen production to halt disease advancement and improve implantation rates during assisted reproductive technology (ART) procedures.
– **Progestin-Only Therapy:** Aids in minimizing lesion regrowth and is frequently utilized for long-term disease management following surgery.
– **Low-Estrogen Combined Oral Contraceptives:** Preferred over high-estrogen variants to curtail lesion growth.
## Nutritional and Lifestyle Interventions
### The Role of an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Dietary changes can assist in diminishing inflammation and oxidative stress, potentially enhancing fertility results. Helpful dietary elements comprise:
– **Omega-3 Fatty Acids:** Present in salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts, these help lessen inflammatory mediators.
– **Antioxidants:** Citrus fruits, bell peppers, green tea, and dark chocolate work to counteract oxidative stress.
– **Curcumin:** A component in turmeric known for reducing inflammation and immune system dysfunction.
– **Low-Glycemic Carbohydrates:** Foods such as quinoa, beans, and sweet potatoes help stabilize blood sugar levels and lower systemic inflammation.
## Diagnosis: MRI vs. Ultrasound in Endometriosis
Precise imaging is vital for effective treatment strategies. The two main diagnostic approaches are:
– **Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):** Highly effective for identifying deep infiltrating endometriosis, particularly in retroperitoneal regions and ovarian endometriomas. However, it is expensive and time-consuming.
– **Transvaginal Ultrasonography (TVUS):** A more accessible and economical initial diagnostic tool, albeit less reliable for identifying peritoneal lesions.
Utilizing a combination of both imaging techniques can improve diagnostic accuracy and assist in customizing treatment plans.
## Fertility Optimization Strategies
### 1. Surgical Intervention
Laparoscopic removal of endometriotic lesions can:
– Alleviate inflammation and discomfort.
– Enhance ovarian functionality.
– Boost chances of spontaneous conception.
Nevertheless, repeated surgeries may adversely affect ovarian reserve, necessitating careful evaluation.
### 2. GnRH Agonist Therapy Post-Surgery
GnRH agonists administered after laparoscopic procedures have been shown to:
– Decrease recurrence rates.
– Improve pregnancy outcomes.
– Balance hormones for enhanced fertility results.
### 3. Ovulation Induction and Intrauterine Insemination (IUI)
For women with mild endometriosis…