Title: Grasping Venous Leak Syndrome: The Hidden Crisis Impacting Men’s Sexual Wellness
Venous Leak Syndrome (VLS) is a condition that progressively affects almost all men — yet it remains predominantly unspoken. This lack of discussion around VLS can hinder timely diagnosis and treatment, impacting not just a man’s sexual health but also his emotional wellbeing and relationships. The encouraging news? For the majority of men, VLS can be managed effectively through straightforward, non-invasive methods — no medication required.
What Is Venous Leak Syndrome?
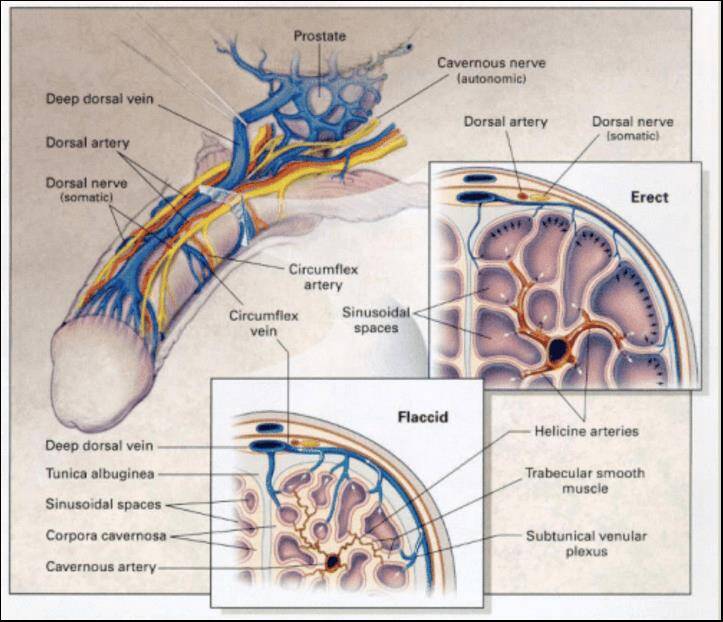
Achieving an erection involves a complex interplay of the brain, nerves, hormones, and blood vessels. A key factor is the ability to trap blood within the penile chambers, which is essential for maintaining firmness. Venous Leak Syndrome manifests when the veins in the penis fail to hold the blood required to sustain an erection. Consequently, men with VLS may find it easy to initiate an erection but face challenges in keeping it.
This condition tends to escalate with age. By around the age of 70, while a man may still be capable of achieving an erection, the structural integrity that helps retain blood in the penis weakens. Aging causes a decline in the smooth muscle tissue, which plays a vital role in constricting veins during an erection. Additionally, veins may become stiffer and lose their ability to stretch. The outcome is a rapid loss of blood, resulting in erections that fizzle out too soon.
Why Does It Happen?
The degradation of smooth muscle tissue and venous stiffness are natural aspects of aging — similar to how hands and feet can swell after prolonged sitting. While skeletal muscles can be fortified through exercise, the health of smooth muscle in the penis depends on regular sexual activity. Contributing factors to VLS include:
– Aging
– Hypertension and diabetes
– Smoking
– Obesity
– Certain medications
– Sedentary lifestyle
– Poor cardiovascular health
Emotional and Physical Repercussions
The ramifications of VLS extend beyond the bedroom. Many men experience a decline in confidence, which may lead to anxiety, depression, and difficulties in relationships. Over time, persistent poor blood retention during erections and “sleep erections” can result in fibrosis — scarring of penile tissues — causing irreversible reduction in penile length and girth.
Diagnosing VLS: The Significance of Early Recognition
Timely detection is pivotal for managing and possibly reversing many consequences of VLS. Men experiencing initial symptoms such as shorter erection duration or difficulty maintaining stiffness during intercourse should consult a urologist. Diagnosis generally involves:
– A comprehensive medical and sexual history
– ED (erectile dysfunction) questionnaires
– Physical examination
– Blood tests
Specialized tests include:
1. Penile Duplex Ultrasound:
A non-invasive procedure employing Doppler ultrasound waves to evaluate blood flow in penile tissues, both pre- and post-erection. It provides clear insights into arterial inflow and venous outflow, assisting in identifying the presence and intensity of VLS.
2. Wearable Erection Monitoring Devices:
Cutting-edge wearable technology, like Bluetooth-enabled erection rings, enables men to evaluate real-life erection quality (firmness and duration) at home, in a relaxed and private environment. This information can be shared with a doctor to offer an objective assessment of progress or decline over time.
Treatment Alternatives for VLS
Many men believe that pills are the sole treatment for erectile dysfunction-related conditions like VLS. However, several non-pharmaceutical and non-surgical alternatives can restore functionality and improve quality of life.
1. Erection Rings:
Safe constriction rings can assist in retaining blood during arousal by limiting venous outflow while allowing arterial inflow. Unlike tight bands that obstruct fresh blood flow and can only be used for 20-30 minutes, newer designs are made for prolonged wear up to 10 hours, supporting firmness safely.
2. Lifestyle Changes:
Enhancing vascular health through weight loss, quitting smoking, implementing a nutritious diet, and regular aerobic exercise can substantially lower the risk or severity of VLS.
3. Medications:
Oral PDE5 inhibitors (such as sildenafil and tadalafil) enhance arterial inflow. However, they do not tackle the fundamental dilemma of VLS — the loss of blood. These medications may work best in conjunction with other treatments like erection rings.
4. Surgery:
In certain cases, surgical options to ligate leaking veins or rectify anatomical vascular issues may provide relief. However, success rates can vary, and surgery is usually reserved for more severe or resistant cases.
5. Penile Prostheses:
As a final alternative, surgically implanted devices offer a lasting resolution for VLS. These devices deliver consistent rigidity and are often considered by individuals who have not responded to medications or other treatments.
Preventing VLS and Sustaining Erections with Age
Although aging is unavoidable, there are strategies to delay or mitigate the severity of VLS:
– Keep a healthy weight
– Manage blood pressure and blood sugar levels
– Avoid smoking and limit alcohol intake
– Engage in regular exercise (particularly cardiovascular activities)
– Maintain regular sexual activity to preserve the health of the penile tissues